Part 4: Measuring Maximal Oxygen Consumption
In this fourth installment of our Introductory Series, we examine how to accurately measure maximal oxygen consumption, as well as discuss some of the implications associated with different testing protocols. What is Maximal Oxygen Consumption? Maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max) describes the body’s ability to uptake and utilize oxygen during intense or maximal full-body exercise. ItContinue reading "Part 4: Measuring Maximal Oxygen Consumption"
In this fourth installment of our Introductory Series, we examine how to accurately measure maximal oxygen consumption, as well as discuss some of the implications associated with different testing protocols.
What is Maximal Oxygen Consumption?
Maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max) describes the body’s ability to uptake and utilize oxygen during intense or maximal full-body exercise. It is formally defined as the maximum integrated capacity of the pulmonary, cardiovascular and muscular systems to uptake, transport and utilize O2, respectively.
Historically, VO2max has been measured by completing an incremental exercise test on a treadmill or cycle ergometer; however, it can now be measured in any training environment with the VO2 Master Analyzer. The VO2max test has become a cornerstone in clinical and applied physiology involving physical exercise.
Considerations for Measuring VO2max
There are dozens of different protocols and means of measuring VO2max across a number of different sports, and there are significant considerations that must be taken into account before completing a test.
1. Protocol Selection
Selecting a measurement protocol depends on such factors as fitness level of the test subject, their preferred sport, and access to appropriate equipment. Novel procedures for testing VO2max have been established for children, adults of varying fitness, obese individuals, and medical patient populations.
It is important to understand the relationship between an athlete’s background and their measured VO2max. For instance, consider three athletes: a runner, a cyclist and a kayaker – all of whom are world class in their respective discipline.
Now, if we have each athlete complete incremental (graded) exercise tests to exhaustion in each of the three different sports, we will observe some interesting results. The kayaker will have a very low VO2max when running and cycling simply because he never uses his legs in training, but his VO2max will be world class when tested in a kayak. Similarly, the runner will have a high value when running and cycling and a low VO2max when tested in a kayak. This result has been verified by independent studies, and it is concluded that sport specificity is a critical factor when measuring VO2max.
This is a significant benefit of the VO2 Master Analyzer, which permits athletes to measure their VO2max in their respective sport, instead of being forced to test only on a treadmill or cycle ergometer.
Graded Exercise Testing (GXT) is the most widely used assessment to examine the dynamic relationship between exercise and integrated physiological systems. Graded Exercise Testing protocols used for testing VO2max are maximal exercise tests where the athlete works to complete exhaustion as speed, power, or incline are increased.
Two common GXT protocols used for many individuals are the Bruce Protocol and the Astrand Protcol. These are both widely used in a clinical environment, have been extensively validated, and possess a wide range of applications for people who are able to tolerate exercise testing on a treadmill.
The differences between the two relate to speed and grade, as identified in Table 1.0.
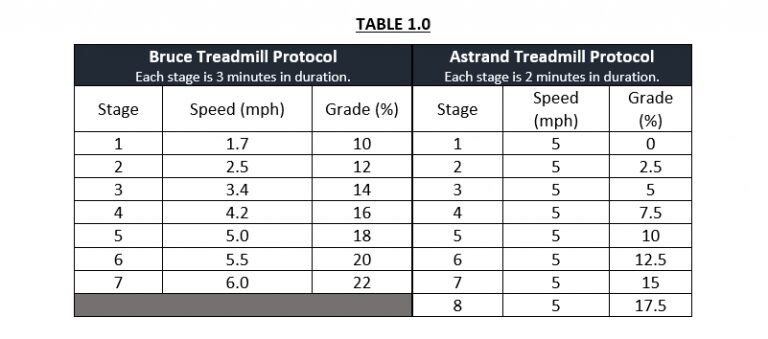
In fact, there are many different incremental protocols that may be used to best fit a specific type of test subject. For instance, the perfect test for a 25-year-old Olympic runner will require a different set-up 60-year-old sedentary individual.
2. Length of The Test
The length of the test is also something to be considered; if it’s set up to be too difficult or too easy for a test subject then it will not produce sought after data.
For example, if a test starts at or beyond a person’s maximum speed, the individual will fail and not reach VO2max; conversely, if a test is too easy, then the subject may eventually tire due to an unnecessary duration of the test itself, and may not reach their true VO2max.
Broadly speaking, a VO2max protocol should ideally fall between 8-12 minutes in duration; however, there are several new protocols that have been developed which now challenge this long held theory.
Please note: Because GXTs are maximal exercise tolerance tests, they require a physician’s clearance and expert supervision. In an untrained individual or an athlete with an underlying heart condition, exercising to a maximal effort can lead to injury or cardiac event.
Future Considerations of Exercise Testing
The information from Graded Exercise Tests can be applied across the spectrum of sport performance, occupational safety screening, research, and clinical diagnostics. The suitability of GXT to determine a valid maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max) has been under investigation for decades. Although a set of recommended criteria exists to verify attainment of VO2max, the methods that originally established these criteria have been scrutinized (M. Beltz et al; 2016). Many studies do not apply identical criteria or fail to consider individual variability in physiological responses.
As an alternative to using traditional criteria, recent research efforts have been directed toward using a supramaximal verification protocol performed after a GXT to confirm attainment of VO2max. Furthermore, the emergence of self-paced protocols has provided a simple, yet reliable approach to designing and administering GXT. Ongoing research continues to examine the utility of self-paced protocols used in conjunction with verification protocols to elicit and confirm attainment of VO2max. Our recommendation is that testing of subjects takes into account all of the above information to help direct you to the most appropriate test for the clients you are working with.
Determining VO2max
Visualizing how the body is responding to increasing exercise intensity/load is always a good first check for a VO2max test. You should see that heart rate and oxygen consumption will increase throughout the test. At the end of the test, you may observe that both heart rate and VO2max begin to level out. When using the VO2 Master Analyzer, the test subject’s VO2max will be determined and displayed via the VO2 Master Manager app, so no additional manual determination is required. This feature can be adjusted based on the protocol design within the app itself.
Summary
When utilizing a VO2 Master Analyzer device, testing maximal oxygen consumption can be straight forward and requires minimal testing equipment. However, in best practice there are some considerations that must be taken into account in order to get accurate and repeatable measures. Some of the key considerations include deciding which test protocol to use, the athlete’s capabilities, and whether the test will be performed in the lab or in the field.
Testing in the athlete’s preferred sport is now possible: get out of the lab and begin exploring the true limits of an athlete’s potential!
—
In the next Beginner Series article, we will explore how VO2max is a key determinant in team sport performance.
